Understanding Skin Discoloration: Causes and Care
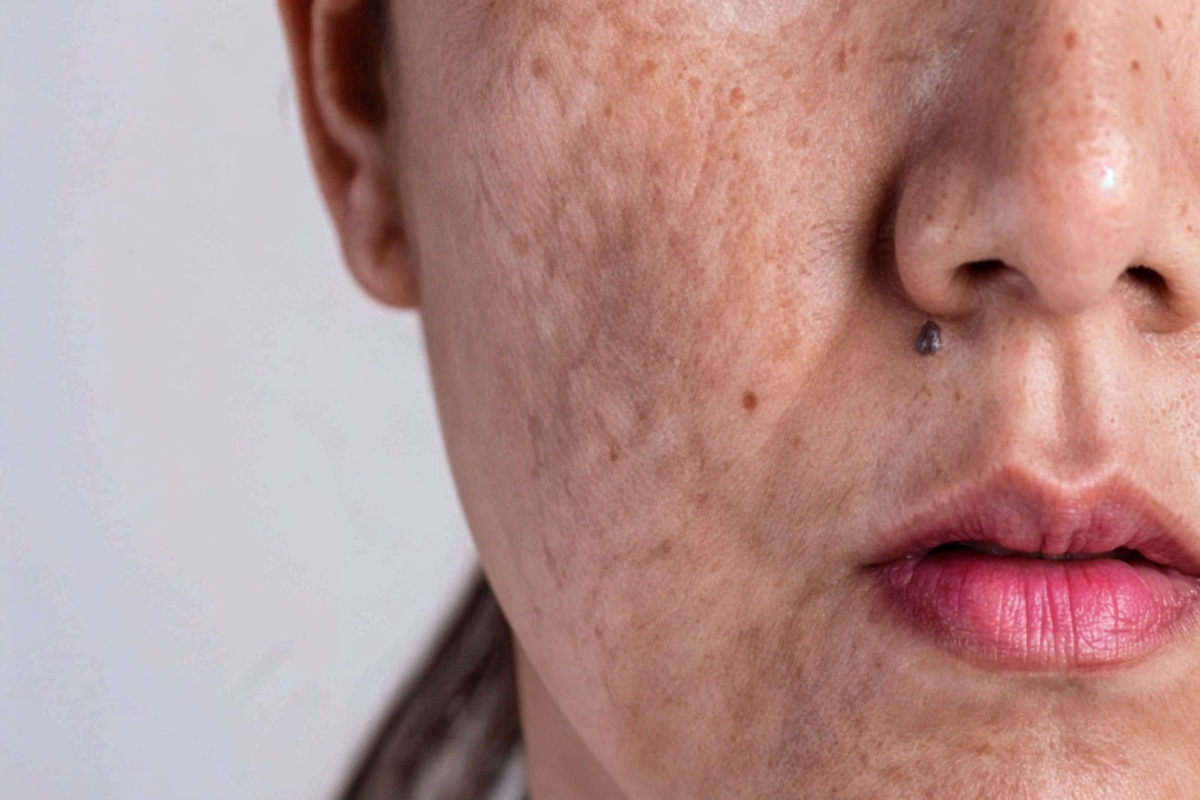

Skin that appears abnormally dark or light deviates from its usual pigmentation and skin discoloration, which can be a concern for many individuals.
What Determines Skin Color?
Skin color is determined by melanocytes, the cells that produce melanin, the pigment responsible for skin color.
Hyperpigmentation: Excess melanin results in darker skin.
Hypopigmentation: Reduced melanin leads to lighter skin.
Depigmentation: Complete absence of melanin causes very light skin.
Causes of Skin Discoloration
Hyperpigmentation
Excess melanin can be caused by several factors:
Skin inflammation: Leads to post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation.
Medications: Certain drugs, including minocycline, some cancer treatments, and birth control pills.
Hormonal disorders: Conditions such as Addison’s disease.
Genetic conditions: Like hemochromatosis, an iron overload disorder.
Sun exposure: Overexposure to sunlight can increase melanin production.
Pregnancy: Melasma, often called the “mask of pregnancy.”
Birthmarks: Some congenital conditions cause hyperpigmentation.
Acanthosis nigricans: Characterized by dark, velvety patches.
Hypopigmentation
A lack of melanin can result from:
Skin inflammation: Leads to post-inflammatory hypopigmentation.
Fungal infections: Such as tinea versicolor.
Pityriasis alba: A common skin condition.
Vitiligo: An autoimmune disorder causing loss of pigment.
Medications: Some drugs can reduce melanin.
Idiopathic guttate hypomelanosis: Small, white spots often found on sun-exposed areas.
Birthmarks: Some congenital conditions cause hypopigmentation.
Managing Skin Discoloration at Home
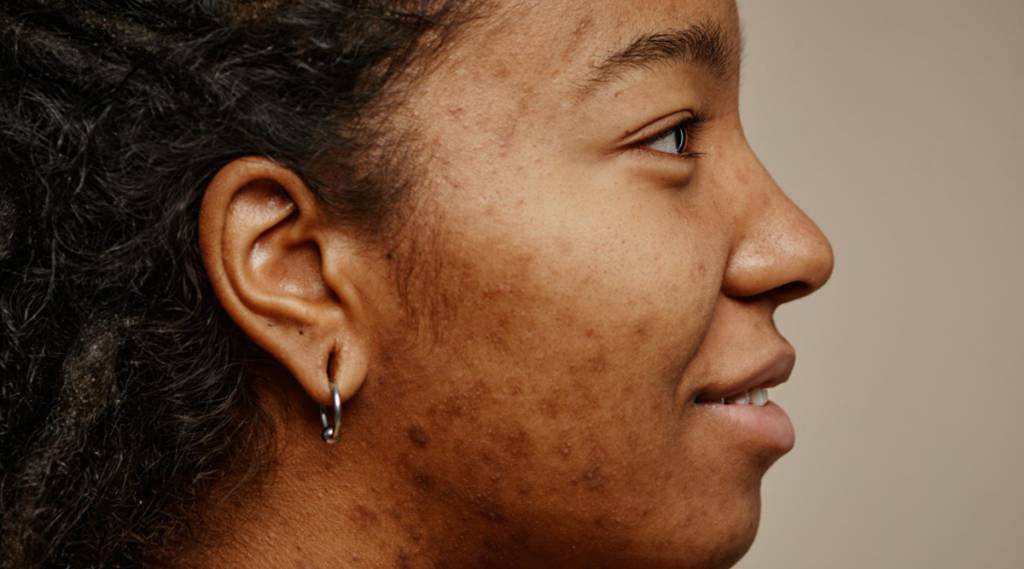
There are both over-the-counter and prescription creams available for lightening hyperpigmented skin. Products containing hydroquinone and tretinoin can be effective but should be used with caution, especially on darker skin, and not for more than three weeks at a time. Cosmetics can also help mask discoloration.
To prevent further discoloration, avoid excessive sun exposure and use a sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher.
When to Seek Medical Advice
Consult a healthcare provider if you experience:
Skin discoloration causing significant concern.
Persistent or unexplained changes in skin color.
Skin sores or lesions that change shape, size, or color, which could indicate skin cancer.
What to Expect During a Medical Consultation
During a medical consultation, your provider will:
Perform a physical exam and ask about your symptoms and medical history.
Inquire about the onset, progression, and spread of the discoloration.
Ask about your medication use, family history, sun exposure habits, and diet.
Check for other symptoms like rashes or skin lesions.
Diagnostic Tests and Treatments
Your healthcare provider may perform various tests, including:
Adrenocorticotrophin hormone stimulation test: To assess adrenal function.
Skin biopsy: To examine skin cells.
Thyroid function studies: To check for thyroid-related issues.
Wood lamp test: To examine skin under ultraviolet light.
KOH test: To identify fungal infections.
Treatment options may include creams, ointments, surgery, or phototherapy. Bleaching creams can lighten dark areas, and some skin color changes may return to normal without treatment.
Understanding the causes and treatments of skin discoloration can help manage these conditions more effectively and improve overall skin health.